English


Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2025-07-10 Origin: Site











Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Profile Extrusions
● What Are T-Slot Aluminum Extrusions?
>> Key Characteristics of T-Slot Extrusions
>> How T-Slot Extrusions Enhance Design Flexibility
● What Are U-Channel Aluminum Extrusions?
>> Key Characteristics of U-Channel Extrusions
>> Functional Roles of U-Channel Extrusions
● Structural and Functional Differences Between T-Slot and U-Channel Extrusions
● Advantages of T-Slot Aluminum Profile Extrusions
● Advantages of U-Channel Aluminum Profile Extrusions
● Additional Considerations When Working with Aluminum Profile Extrusions
● Choosing Between T-Slot and U-Channel Extrusions
● FAQ
>> 1. What industries commonly use T-slot aluminum extrusions?
>> 2. Can U-channel extrusions be used for structural frameworks?
>> 3. Are T-slot and U-channel extrusions interchangeable?
>> 4. What materials are typically used for these extrusions?
>> 5. How do I choose between metric and imperial T-slot extrusions?
When it comes to aluminum profile extrusions, two common types often discussed are T-slot extrusions and U-channel extrusions. Both have unique designs and applications, making them suitable for different structural and assembly needs. Understanding their differences is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers who rely on aluminum extrusions for building frameworks, machinery, furniture, and automation systems.

Aluminum profile extrusions are long, shaped aluminum bars created by pushing molten aluminum through a shaped die. This process results in profiles with specific cross-sectional geometries designed to meet various functional requirements. These extrusions are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly versatile, making them popular in industries ranging from construction to robotics.
Among the many extrusion profiles, T-slot and U-channel are widely used due to their modularity and ease of assembly. However, their structural features and intended uses differ significantly.
T-slot aluminum extrusions feature a distinctive "T"-shaped groove running along one or more sides of the profile. This groove is designed to accept specialized fasteners such as T-nuts and bolts, which slide into the slot to secure accessories or connect multiple extrusions together.
- Modular Design: The T-shaped slots allow for easy assembly and disassembly of frameworks without welding or permanent fastening.
- Versatility: T-slot extrusions can be combined with a wide range of accessories like brackets, hinges, panels, and connectors to build complex structures.
- Strength and Durability: Typically made from anodized 6063-T5 or T6 aluminum, these extrusions offer a good balance of strength and lightweight properties.
- Common Applications: Workstations, machine guards, automation equipment, furniture, and laboratory enclosures.
- Multiple Slot Configurations: Profiles may have one to four T-slots on different faces, allowing for multi-directional assembly.
The T-slot system is often referred to as an "industrial erector set" because it enables quick prototyping and customization of mechanical assemblies.
One of the most significant advantages of T-slot aluminum profile extrusions is their ability to be reconfigured quickly. Designers and engineers can modify existing frameworks by simply loosening a few bolts and repositioning components. This flexibility reduces downtime in manufacturing and allows for iterative design improvements without the need for costly re-fabrication.
Moreover, the T-slot system supports a wide variety of accessories such as end caps, joining plates, hinges, and casters. This accessory ecosystem expands the possibilities of what can be built, from simple frames to complex robotic arms or conveyor systems.
U-channel extrusions have a simple U-shaped cross-section, resembling a channel or a trough. Unlike T-slot profiles, U-channels do not have a groove designed to accept sliding nuts or bolts. Instead, they provide a structural channel that can be used for guiding, housing, or framing purposes.
- Simple Geometry: The U shape provides a channel that can hold panels, glass, or other materials securely.
- Structural Support: Often used as edge trims, frames, or tracks where a slot is not required.
- Ease of Fabrication: U-channels can be cut, bent, or drilled to fit specific applications.
- Common Applications: Window and door frames, protective edging, cable management, and linear guides.
- Less Modular: U-channels generally require welding or additional fasteners for assembly, lacking the integrated fastening system of T-slot profiles.
U-channel aluminum profile extrusions excel in applications where a simple channel is needed to hold or guide other components. For example, in construction, U-channels are often used as framing elements for windows and doors, where they provide a secure edge for glass panes or panels.
In industrial settings, U-channels can serve as cable trays or protective edging to shield wiring and hoses from damage. Their open channel design makes them ideal for applications where components need to slide or be inserted easily.

| Feature | T-Slot Extrusions | U-Channel Extrusions |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Section Shape | Square or rectangular with T-shaped slots | U-shaped channel without slots |
| Assembly Method | Uses sliding T-nuts and bolts for modular assembly | Typically requires welding, screws, or rivets |
| Modularity | Highly modular and reconfigurable | Limited modularity, more permanent assembly |
| Load Bearing | Designed for framing and structural support | Used mainly for housing or guiding components |
| Accessories Compatibility | Wide range of compatible connectors and accessories | Limited accessory options |
| Typical Applications | Machine frames, automation, workstations | Window frames, cable trays, edge protection |
- Flexibility: Easily reconfigured or expanded without specialized tools.
- Speed of Assembly: No welding required; parts can be assembled with simple hand tools.
- Customization: Compatible with a broad ecosystem of accessories.
- Aesthetic Finish: Anodized or powder-coated finishes available for corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Lightweight and Strong: Suitable for medium-duty structural applications.
- Reduced Maintenance: Since assemblies can be adjusted without permanent joints, maintenance and upgrades are simplified.
- Simplicity: Easy to manufacture and install for straightforward applications.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive due to simpler design.
- Good for Enclosures: Ideal for holding panels or glass securely.
- Versatility in Fabrication: Can be bent or shaped as needed.
- Robust Edge Protection: Provides excellent protection for edges of materials, reducing wear and damage.
Both T-slot and U-channel extrusions are typically made from aluminum alloys such as 6063-T5 or 6063-T6. These alloys offer good corrosion resistance, excellent surface finish, and sufficient mechanical strength for most structural applications. Anodizing or powder coating further enhances durability and aesthetic appeal.
Aluminum profile extrusions perform well in various environments, including outdoor and humid conditions, due to their corrosion resistance. However, when used in highly corrosive environments such as marine or chemical plants, additional protective coatings or alternative materials may be necessary.
T-slot extrusions require precise machining to maintain the integrity of the slots and ensure compatibility with fasteners. U-channel extrusions, due to their simpler shape, are easier to cut, bend, and weld, making them suitable for custom fabrication projects.
While T-slot extrusions offer superior modularity and ease of assembly, they tend to be more expensive due to their complex cross-sectional design and accessory ecosystem. U-channels, being simpler, are generally more affordable but may incur additional costs if welding or permanent fastening is required.
The decision to use T-slot or U-channel aluminum profile extrusions depends on the project requirements:
- If modularity, ease of assembly, and versatility are priorities, T-slot extrusions are the better choice.
- For simple framing, panel holding, or guiding applications where modularity is less critical, U-channels may be more suitable.
- Consider the load requirements: T-slot extrusions generally provide better structural strength for frameworks.
- Factor in cost and complexity: U-channels can be more economical for simple uses but may require welding or permanent fasteners.
- Evaluate the need for future modifications: T-slot systems allow for easy changes, while U-channel assemblies tend to be more permanent.
T-slot and U-channel aluminum profile extrusions serve distinct roles in manufacturing and construction. T-slot extrusions are renowned for their modularity, adaptability, and ease of assembly, making them ideal for building complex, adjustable frameworks. U-channel extrusions offer a simpler, more economical solution for applications requiring a channel or guide but without the need for modular fastening systems.
Understanding these differences enables designers and engineers to select the appropriate extrusion type for their specific needs, optimizing both performance and cost-effectiveness in their projects. Whether building a sophisticated automation system or a simple frame, choosing the right aluminum profile extrusion is key to success.
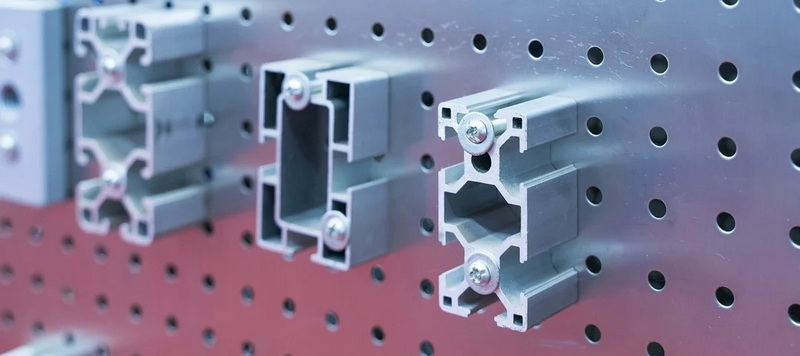
T-slot extrusions are widely used in automation, manufacturing, laboratory equipment, furniture construction, and safety guarding due to their modularity and strength.
While U-channels provide some structural support, they are generally not designed for heavy-duty frameworks and lack the modular fastening system of T-slots.
No, they are not interchangeable because their cross-sectional shapes and assembly methods differ significantly, affecting compatibility with accessories and connectors.
Both T-slot and U-channel extrusions are commonly made from anodized 6063-T5 or T6 aluminum, which offers good strength, corrosion resistance, and finish quality.
Metric profiles are common internationally and in scientific applications, while imperial profiles dominate North America. Hardware compatibility should guide the choice to ensure matching fasteners and accessories.
Stainless Steel Grades 201 Vs 304: Cost Vs Performance Breakdown
316L Vs 316 Stainless Steel Grades: Which Is Better for Corrosion Resistance?
Comparing Austenitic Vs Martensitic Stainless Steel Grades: What You Need To Know?
Stainless Steel 430 Vs 304: Key Differences Explained for Manufacturers
304 Vs 316 Stainless Steel Grades: Which One Suits Your Project Best?
Stainless Steel Pipes Vs Galvanized Pipes: Durability And Cost Analysis
Comparing Stainless Steel Pipes And PVC Pipes: What You Need To Know?
Stainless Steel Pipes Vs Copper Pipes: Pros And Cons for Industrial Use
Seamless Stainless Steel Pipes Vs Welded Pipes: Key Differences Explained
Stainless Steel Pipes Vs Carbon Steel Pipes: Which One Suits Your Project?
